What is Naloxone (Narcan)?
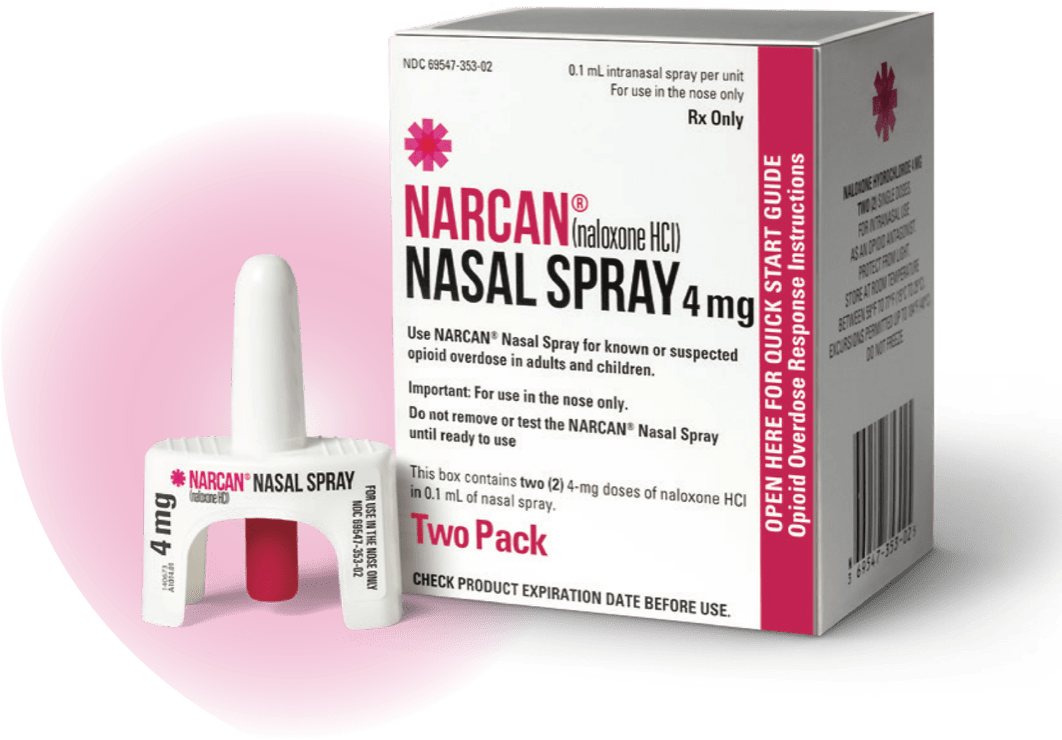
Naloxone – also called Narcan – is a medication designed to rapidly reverse opioid overdose. It is available in three FDA-approved formulations: injectable, autoinjectable, and prepackaged nasal spray.
Naloxone should be administered when a patient is showing signs of opioid overdose.
Pregnant women can be safely given naloxone in limited doses under the supervision of a doctor.
Naloxone is NOT effective in treating overdoses of benzodiazepines, barbiturates, clonidine, GBH, ketamine, and stimulant overdoses (cocaine and amphetamines, including methamphetamine and MDMA).

If opioids are taken in combination with sedatives or stimulants, using Naloxone may be helpful in reversing an overdose.
If an overdose of fentanyl is suspected, Naloxone should be used.
However, due to the increased potency of fentanyl and fentanyl-analogs compared to that of heroin, a higher dose of Naloxone may be needed to reverse the overdose and induced respiratory depression.
Candidates for Naloxone
Candidates for naloxone are those who:
- Take high doses of opioids for long-term management of chronic pain
- Receive rotating opioid medication treatments
- Have been discharged from emergency medical care following opioid
poisoning or intoxication - Take certain extended-release or long-acting opioid medications
- Are completing mandatory opioid detoxification or abstinence programs
Storing Naloxone
Storage of Naloxone:
Store naloxone in a safe and quickly accessible place at room temperature and protected from light.
Keep all medicine in a safe place where children or pets cannot reach it.
For more information on Naloxone, visit:
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patientsand-providers/information-about-naloxone

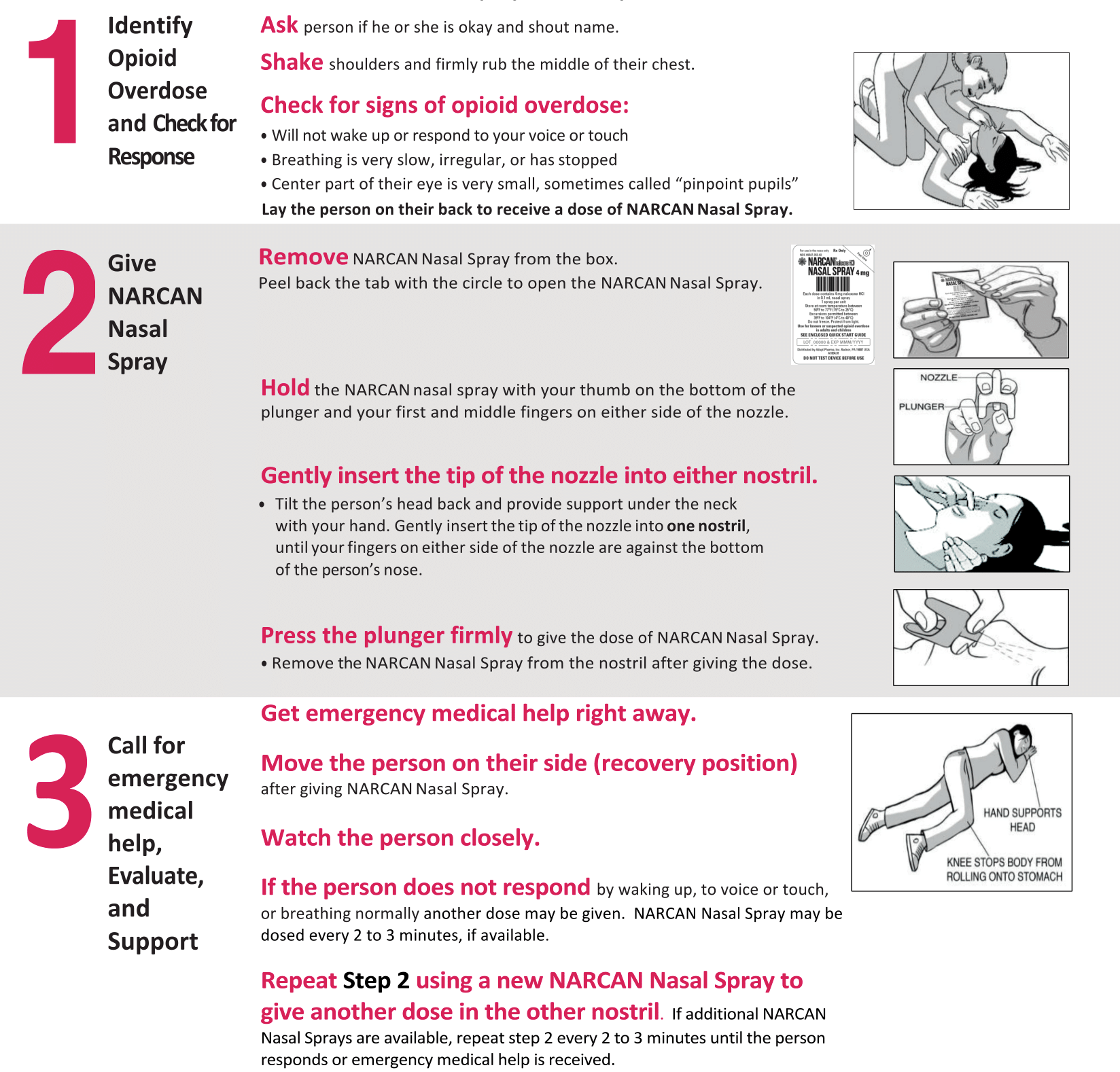
How to Give Naxolone Nasal Spray